GDPR – Six steps all companies can take now
Northdoor outlines the key obligations and proposes six steps to help you kick-start the compliance process.
First things first: In very simple terms, the key implication of GDPR is that your business must fully understand what personal data it holds on EU citizens, where this data is stored and who has access to it, throughout the full information lifecycle.
You need to ensure that key decision-makers within your organisation are aware of the legislation and its potential impact. Implementing GDPR could have place significant demands on your organisation.
Once the right people in your organisation are aware of GDPR and its implications, you’re ready to tackle the first step: determining the information you hold.
Step one: the information you hold
Under GDPR, any information that could conceivably identify a person must be protected against loss or exposure. The challenge for businesses is to work out what data they hold and in which systems – both paper-based and electronic. In a networked world, you must also think about data you own and have shared with partners. The first stage in step one is simply to start the conversation with the business people who own the data and start to work out exactly what you have.
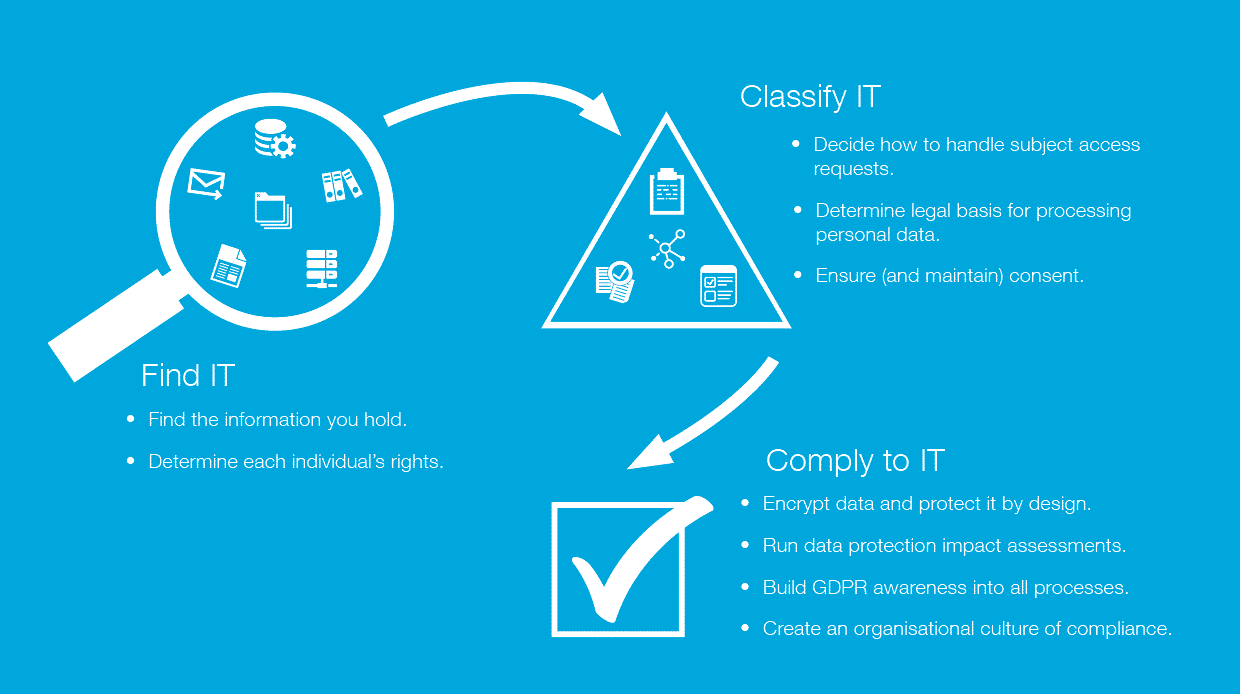
At Northdoor, we call this stage Find IT. Once you’ve found the data, you can Classify IT, and then you will need to create the right compliance structures around people, processes and technology: Comply to IT.
Even if you haven’t yet precisely determined data ownership or risk, you can use simple solutions to encrypt everything at step one. GDPR requires you to protect data in the event of accidental loss, and full encryption is a fast and easy way to address this.
Step two: individuals’ rights and consent
Once you have established what personal data you hold and taken the first steps to protect it through encryption, you should move on to understand the rights that individuals have over their data under GDPR. In short, these are: to access the data, have inaccuracies corrected, have some or all information erased, have it transferred to another organisation, have it removed from marketing lists and have it protected from automated profiling. Naturally, you will need to have measures in place for responding to requests to access, amend, transfer or delete data, and you will need to understand the legal deadlines.
This is also a good point at which to consider how you seek, obtain and record consent from individuals to hold their data. Under GDPR, consent must be a positive agreement – you may need to review your processes and put in place an effective audit trail for demonstrating that consent has been given.
Step three: subject access requests
GDPR introduces new rules for dealing with subject access requests, and you will need to consider whether your existing procedures should change. Building on the initial work in step two, you should consider how you will comply with access requests, and you may also want to establish policies for rejecting unfounded or excessive requests for access or changes.
If it is likely that your organisation will need to deal with large numbers of access requests, you should consider creating an automated, self-service portal as a way to reduce logistical costs and delays.
Step four: the legal basis for processing personal data
As you examine the different types of processing you carry out on personal data, GDPR requires you to identify and document the legal basis for that processing. Unlike the existing DPA legislation, GDPR modifies some rights depending on the legal basis for processing. For example, individuals will have a stronger right to request deletion of their data in cases where you use consent as your legal basis for processing.
There is overlap between the legal bases in GDPR and DPA, which should simplify this fourth step. For all activities, you should take care to document all actions, decisions and policies to help you comply with accountability requirements under GDPR.
Step five: data breaches
Some organisations are already required to notify the ICO and/or other bodies when there is a personal data breach. Under GDPR, breach notification will apply universally to all organisations – though only those breaches where the individual is likely to suffer some form of damage will need to be notified.
During this step, you should ensure that you have the right procedures in place to detect, investigate and report on personal data breaches. You will need to have the ability to notify individuals impacted by the breach within set timescales, and you should be aware that failure to follow breach-reporting guidelines could result in an additional fine on top of any penalty levied for the breach itself.
Step six: data protection by design and Data Protection Impact Assessments
The ICO has provided detailed guidelines on Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs) which show how they can link to organisation processes such as risk management and project management. All companies should consider which scenarios may necessitate a data PIA (DPIA) and how such an exercise would be run.
In the past, a “privacy by design” approach to personal data was always considered best practice, and an implicit element in data protection. Under GDPR, it will become an explicit legal requirement, and as a result you will need to verify that such an approach is embodied in your standard practices.
Industrialise your GDPR programme for faster, more assured compliance
To find out how Northdoor can help you achieve GDPR compliance faster and more effectively, please contact us for an informal assessment. We’ll review your existing approaches to data protection and security, and provide a clear checklist of recommended next actions, helping you get started quickly.
Find out more
Source: 2015 Cost of Data Breach Study: United Kingdom, IBM and Ponemon Institute